
In today’s rapidly advancing technological landscape, surveillance systems play a crucial role in ensuring safety and security. Digital Video Recorders (DVR) and Network Video Recorders (NVR) are two fundamental components of modern surveillance setups. Understanding the differences, functionalities, and advantages of DVR and NVR can help individuals and businesses make informed decisions when choosing the appropriate system for their needs. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of DVR and NVR, highlighting their features, applications, and benefits.
What is DVR and NVR?
DVR and NVR are both devices used to record and store video footage, but they differ in how they process and manage the data.
DVR (Digital Video Recorder).
DVR stands for Digital Video Recorder. It is a surveillance system that converts analog video signals from security cameras into digital format for storage and viewing. The captured video footage is compressed and stored locally on the DVR’s hard drive.
Read in Detail about DVR
NVR (Network Video Recorder).
NVR, on the other hand, stands for Network Video Recorder. It is a more advanced surveillance solution that processes and stores IP (Internet Protocol) camera footage. NVRs operate over a network and are capable of handling higher-resolution video streams.

DVR and NVR: A Detailed Comparison.
To understand the distinctions between DVR and NVR better, let’s compare them across various aspects:
|
Feature |
DVR |
NVR |
|
Signal Processing |
Analog Cameras |
IP Cameras |
|
Video Quality |
Limited by Analog Technology |
High-resolution IP Cameras |
|
Camera Distance |
Limited due to Analog Signals |
Longer Distances with IP Cameras |
|
Network Dependency |
Not Network Dependent |
Operates Over a Network |
|
Resolution Support |
SD, HD 720p |
Full HD, Ultra HD, 4k |
|
System Scalability |
Limited Scalability |
Highly Scalable |
|
Remote Viewing |
May Require Additional Hardware |
Easy Remote Access |
|
Video Compression |
MPEG-4 or H.264 |
H.264, H.265, H.265+ |
Read More about Difference between Analog cameras and IP cameras
Benefits of DVR.
DVRs have been widely used in the past and continue to offer several advantages:
- Cost-Effective: DVR systems are generally more budget-friendly, making them a suitable choice for smaller surveillance setups.
- Ease of Use: These systems are easy to set up and operate, making them ideal for non-technical users.
- Reliable Local Storage: DVRs store footage locally, ensuring continuous recording even in case of network disruptions.
- Compatibility: DVRs can work with existing analog cameras, making them a practical upgrade option for older surveillance systems.
Benefits of NVR.
With advancements in technology, NVRs have gained popularity and come with their own set of advantages:
- High-Quality Video: NVRs support high-resolution IP cameras, offering clearer and more detailed video footage.
- Flexible Remote Access: Users can access live and recorded video remotely through smartphones and other devices.
- Scalability: NVRs can easily accommodate additional IP cameras, providing room for future expansion.
- Intelligent Analytics: Some NVRs offer advanced analytics features, such as facial recognition and motion detection.
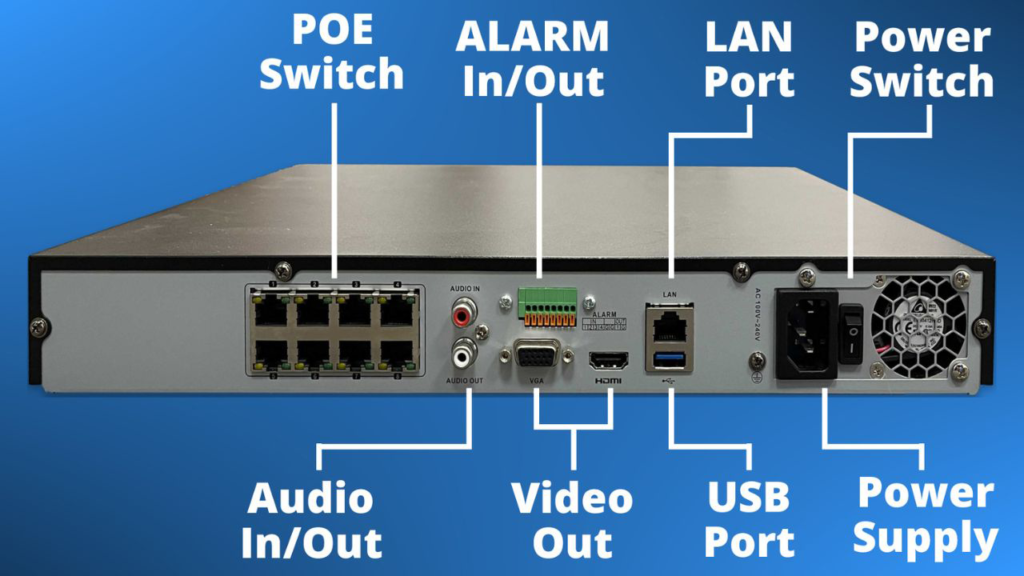
Applications of DVR and NVR.
Both DVR and NVR systems find applications in various settings:
DVR Applications:
- Small Retail Stores
- Residential Properties
- Restaurants and Cafes
- Small Offices
NVR Applications:
- Large Commercial Complexes
- Industrial Facilities
- Government Buildings
- Casinos and Entertainment Venues
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing between DVR and NVR.
When deciding between DVR and NVR systems, several factors should be taken into account:
- Existing Infrastructure: Assess whether you have analog cameras in place or if you are looking to upgrade to IP cameras.
- Budget: Consider your budget constraints and determine the most cost-effective option.
- Video Quality Requirements: Determine the level of video quality needed for your surveillance needs.
- Scalability: Evaluate the potential for future expansion and choose a system that can accommodate your growth.

Some of the latest advancements in DVR technology.
The field of Digital Video Recorders (DVR) has seen significant advancements in recent years, driven by rapid technological progress. These innovations have revolutionised the way surveillance systems operate and enhanced their capabilities. Here are some of the latest advancements in DVR technology:
- High Definition (HD) Recording: The latest DVR systems now support high-definition video recording. With HD resolution, users can capture clear and detailed footage, making it easier to identify objects and individuals.
- H.265 Video Compression: H.265, also known as High-Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC), is a more advanced video compression standard. It significantly reduces file sizes without compromising video quality, allowing for more extended storage of high-resolution video.
- Cloud Storage Integration: Some modern DVRs offer integration with cloud storage services. This enables users to store their video footage securely on remote servers, providing an extra layer of backup and protection against data loss.
- Mobile App Integration: Advanced DVR systems now come with dedicated mobile apps that allow users to access live and recorded video remotely from their smartphones or tablets. This feature is especially beneficial for remote monitoring and on-the-go surveillance.
- Intelligent Video Analytics: DVRs equipped with intelligent video analytics can automatically detect and flag suspicious activities. These analytics features may include motion detection, facial recognition, object tracking, and more.
- Power over Ethernet (PoE) Support: PoE technology allows both data and power to be transmitted over a single Ethernet cable, simplifying the installation process and reducing the need for additional power sources.
- Real-Time Notifications: Some DVRs are equipped with real-time notification capabilities. Users can receive alerts on their mobile devices or via email whenever predefined events, such as motion detection, occur in the monitored area.
- Smart Search and Playback: Advanced search algorithms in modern DVRs enable users to find specific events or incidents quickly. This includes the ability to search based on date, time, motion, or other parameters.
- Remote Configuration and Management: With remote configuration and management options, users can adjust DVR settings and perform updates from anywhere with an internet connection, streamlining maintenance and troubleshooting.
- Network Integration: Modern DVR systems are designed to integrate seamlessly with existing network infrastructures, enabling easy integration with other security systems and devices.
- Extended Storage Capacity: Newer DVR models offer support for larger storage capacities, accommodating the ever-increasing amounts of video data generated by high-resolution cameras.
- Enhanced Cybersecurity: As cybersecurity concerns grow, DVR manufacturers are implementing advanced security measures to protect against unauthorised access and data breaches.
- Integration with Smart Home Devices: Some DVRs can now be integrated with smart home devices, allowing users to control their surveillance systems through voice commands or home automation platforms.
These advancements in DVR technology have greatly improved the effectiveness and versatility of surveillance systems, empowering individuals and businesses to enhance their security and safety measures. As technology continues to progress, we can expect even more exciting developments in the field of DVRs in the future.

Some of the latest advancements in NVR technology?
The field of Network Video Recorders (NVR) has witnessed significant advancements, driven by the rapid evolution of network technology and the increasing demand for sophisticated surveillance solutions. These advancements have expanded the capabilities of NVRs, making them more powerful and versatile. Here are some of the latest advancements in NVR technology:
- 4K and Ultra-High Definition (UHD) Recording: Modern NVRs now support 4K and Ultra-High Definition (UHD) video recording. This enables the capture of incredibly detailed and sharp video footage, providing enhanced clarity for surveillance purposes.
- H.265+ Video Compression: NVRs equipped with H.265+ video compression technology can significantly reduce video file sizes without compromising image quality. This allows for more efficient storage and reduces bandwidth requirements for remote viewing.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Deep Learning: NVRs with AI and deep learning capabilities can perform advanced video analytics and object recognition. These systems can detect and classify objects, identify individuals, and even analyse behaviour patterns.
- Edge Storage Support: Some NVRs come with edge storage capabilities, allowing them to record video directly onto SD cards or USB drives in IP cameras. This feature ensures continuous recording even if the network connection is lost.
- Cloud Integration: NVRs now offer seamless integration with cloud storage services. This allows users to back up critical video footage to remote servers, providing an additional layer of data redundancy and protection against local hardware failures.
- Enhanced Cybersecurity: With growing cybersecurity threats, NVR manufacturers have implemented robust security protocols to safeguard against unauthorised access and hacking attempts.
- Smart Search and Event Detection: Advanced search algorithms in NVRs enable users to quickly find specific events or incidents within vast amounts of recorded video. Event detection features can trigger alarms or notifications based on predefined criteria.
- Multiple Video Streams: Modern NVRs can handle multiple video streams from various cameras simultaneously. This allows for live viewing, recording, and remote access without compromising performance.
- Intelligent PTZ (Pan-Tilt-Zoom) Control: Some NVRs offer intelligent PTZ control, which automatically tracks moving objects or individuals, ensuring they stay within the camera’s frame.
- Video Wall Support: NVRs with video wall support enable users to display multiple camera feeds on a large screen for enhanced monitoring and situational awareness.
- Integration with Access Control Systems: NVRs can be integrated with access control systems, allowing for a unified security solution where video footage is linked to access events, providing a more comprehensive view of security incidents.
- Redundant Power Supplies: High-end NVR models may come with redundant power supplies to ensure continuous operation even in the event of power failures.
- Mobile and Web Applications: Advanced NVRs offer feature-rich mobile apps and web interfaces, enabling users to access live and recorded video from their smartphones, tablets, or computers.
These advancements in NVR technology have expanded the capabilities of modern surveillance systems, making them more efficient, intelligent, and user-friendly. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect further innovations that will further enhance the effectiveness of NVRs in meeting the security needs of various applications.

FAQs (Frequently asked questions)
1. Are DVR and NVR interchangeable?
No, DVR and NVR are not interchangeable as they are designed for different types of cameras and operate on different technologies.
2. Can I use IP cameras with a DVR system?
No, DVRs are specifically designed for analog cameras and do not support IP camera technology.
3. Can I mix DVR and NVR systems in the same setup?
It is not recommended to mix DVR and NVR systems in the same surveillance setup as they use different signal processing methods.
4. Which system is better for high-resolution recording?
NVRs are better suited for high-resolution recording due to their support for IP cameras with advanced image quality.
5. Is remote access possible with DVR systems?
Yes, remote access is possible with some DVR systems, but it may require additional hardware and setup.
6. Do NVRs require an internet connection for local recording?
NVRs can function without an internet connection for local recording, but remote access requires internet connectivity.

Conclusion.
In conclusion, DVR and NVR are vital components of modern surveillance systems, each offering distinct advantages based on the user’s needs. DVRs are budget-friendly and ideal for smaller setups, while NVRs provide higher video quality and scalability for more extensive applications. Understanding the differences and applications of DVR and NVR will help you make an informed decision when selecting the best surveillance system for your requirements. Stay informed, prioritise security, and choose wisely.

